Specific Heat of Gas
Specific Heat of Gas: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Mayer's Relation, Molar Specific Heat Capacities in Terms of Gas Constant, Relation Between Molar and Principal Specific Heat Capacities & Principal Specific Heat Capacity of a Gas at Constant Pressure etc.
Important Questions on Specific Heat of Gas
The molar specific heat capacity of a mixture of two gases depends on the total number of moles of the two gases.
Derive the formula for the molar specific heat capacity at constant volume of a mixture of two gases.
At a given temperature, the specific heat of a gas at constant pressure is always greater than its specific heat at constant volume.
Specific heat of an ideal gas at constant volume and at constant pressure are related to universal gas constant are as
An ideal monatomic gas is carried along the cycle as shown in the figure. The total heat absorbed in this process is
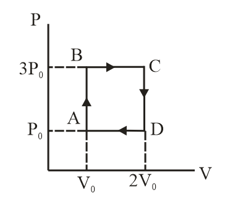
For the next three questions
An ideal diatomic gas is expanded so that the amount of heat transferred to the gas is equal to the decrease in its internal energy.
The molar specific heat of the gas in this process is given by C whose value is
Two mole of oxygen is mixed with eight mole of helium. The effective specific heat of the mixture at constant volume is _____.
Two moles of a certain gas at a temperature, are cooled isochorically so that the pressure of the gas gets reduced by times. Then, as a result of isobaric process, the gas is allowed to expand till its temperature gets back to the initial value. Find the total amount of heat absorbed by gas in this process.
Which of the following is correct for a gas with, and .
(Take, .)
Two moles of oxygen is mixed with eight moles of helium. The effective specific heat of the mixture at constant volume is
The specific heat of helium at constant volume is 12.6 . The specific heat of helium at constant pressure in is about (Assume the temperature of the gas is moderate, universal gas constant, )
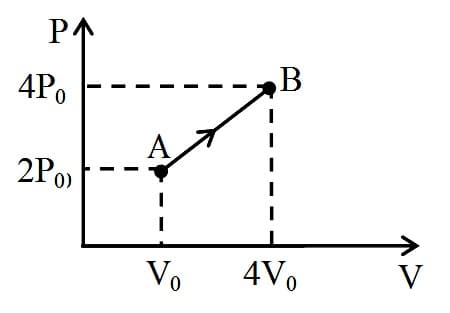
One mole of a monoatomic ideal gas undergoes the process, as in the given diagram. The specific heat for this process is
Assertion: The specific heat at constant pressure is greater than the specific heat at constant volume i.e., .
Reason: In case of specific heat at constant volume, the whole of heat supplied is used to raise the temperature of one mole of the gas through while in case of specific of heat at constant pressure, heat is to be supplied not only for heating 1 mole of gas through but also for doing work during expansion of the gas.
If is the ratio of specific heats and is the universal gas constant, then the molar specific heat at constant volume is given by
Universal gas constant is
For a gas, the difference between the two principle specific heats is 4150 . What is the specific heat of the gas at constant volume if the ratio of specific heat is 1.4?
One mole of an ideal gas requires 207 J heat to raise the temperature by 1K, when heated at constant pressure. If the same gas is heated at constant volume to raise the temperature by the same range, the heat required will be (Take )
For nitrogen and for argon, . The relation between and is given by ( where Cp and Cv are molar specific heats )
Value of two principle specific heats of a gas in determined by different students are given. Which is most reliable?
